

In medical and health education, how is Biotandem used?
While clinical medicine may seem complex, you've all witnessed the power of experience in solving problems in daily practice during clinical training under the supervision of attending physicians and faculty members. Those using Biotandem add knowledge and experience to clinical evaluations and service planning through the simple steps.
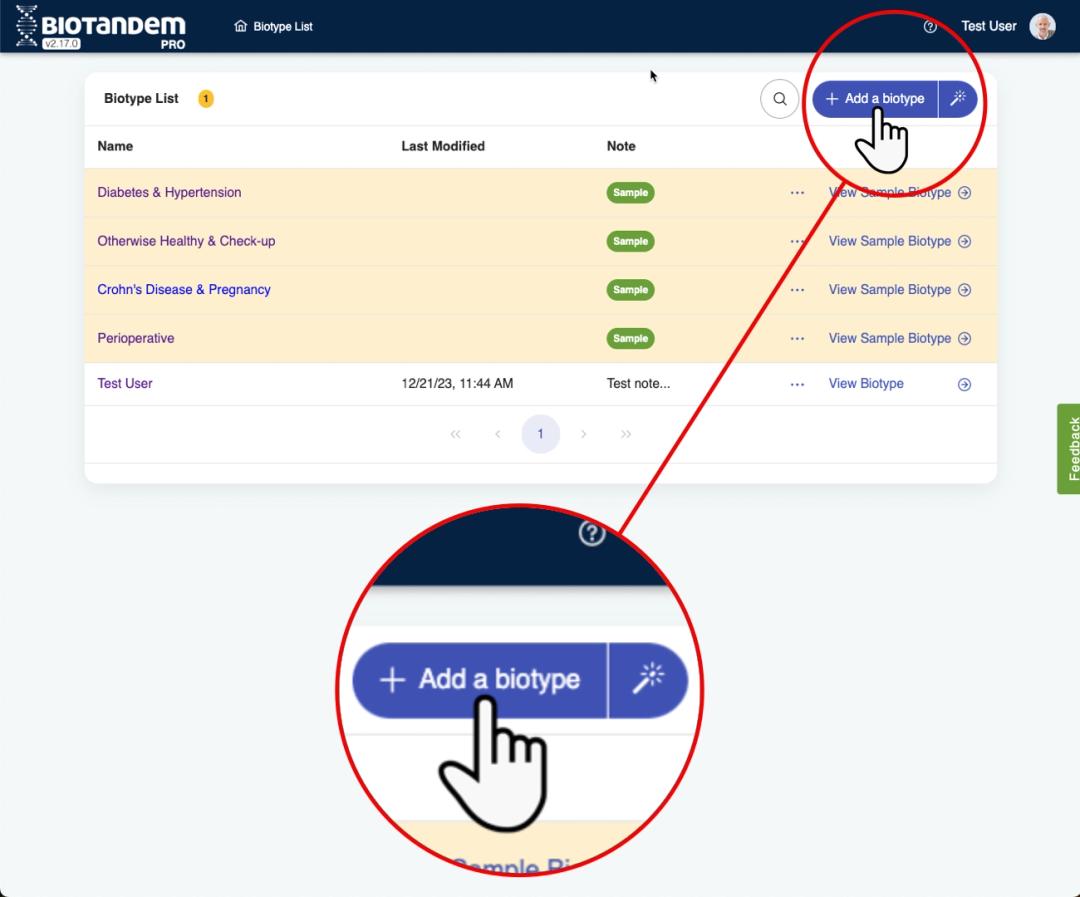
Create a Biotwin
- Create a biotwin (patient profile) consisting of conditions such as diseases, medications, surgical interventions, tests, imaging, family history, allergies, and current problems using the search bar or wizard.
- Review and add important details by clicking on the details icon on the left side of conditions. In these details, find information about disease activity, stage, course, medication complications, and previous usage experiences. Under the 'Tools' section, discover definitions, classifications, and staging criteria for that condition. Check conditions in the search bar if you can't find them in the details.
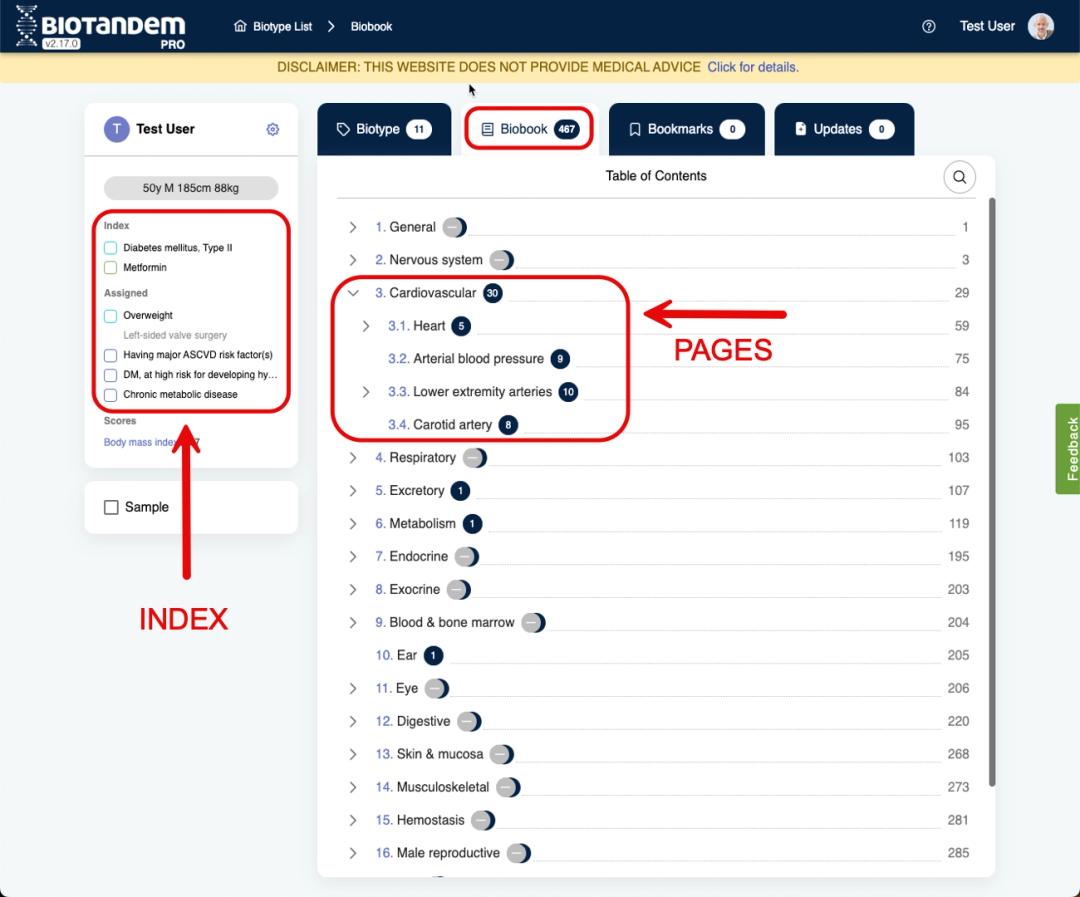
Review the Biobook
- Go to the Biobook tab to review what should and should not be done for this biotwin based on bodily organs or life domains.
- Users can take different approaches here. Either select a body organ or life activity from the table of contents, evaluate pooled recommendations, or choose one or multiple conditions from the index to review only the biobook pages related to them.
- The index method may reveal a connection between conditions, indicating a relationship or drug interaction.
- To review information about preparations, methods to collect specimens, and interpretation of results for a test, add a condition with a 'testing' suffix to the biobook and access the relevant pages.

Make a Service Plan
- If you want to prepare a service plan for that biotwin by reviewing the Biobook, add pages you find important for the plan to the bookmark section within the Biobook. You can view these pages collectively by clicking on the Bookmark tab.
- Please note that your biobooks are subject to change on a daily or weekly basis due to newly added or updated guidelines.
Biotandem offers opportunities to easily grasp certain concepts in medicine:

Whole-Body Approach
Easily see how a holistic approach can be for a biotwin, as its biobook consists only of information related to that biotwin. This way, you can collectively review what needs to be done for all medical divisions.

Tailored Medicine
By observing the instant change in Biobook information when a condition is added or removed, better understand the concept of personalized or tailored medicine. The reason behind the motto 'There is no disease; there is a patient' lies here.

Preventive Medicine
By examining pages labeled as 'Think/risk' or 'Think/monitor' within the Biobook for each bodily organ, better understand the concept of risk management and preventive medicine.

Evidence Based Medicine
By reviewing the evidence levels and grades of recommendation on Biobook pages, better understand the concept of evidence-based medicine.

State of the Art Medicine
By examining the differences between guidelines of various medical associations or countries, you will see how medical approaches can change due to the 'art of medicine' or in limited resource situations.

Continuous Medical Education
By following updates, you can observe how guidelines from new clinical research change and understand the reason behind the concept of continuous medical education.
For Education Coordinators or Instructors:
Utilize Biotandem with an enterprise membership to establish and implement educational standards in the following way:
- Create biotwins (Case vignettes) containing conditions tailored to the student level.
- Review the biobooks of these biotwins and hide pages that are not suitable for the student level.
- Share these biotwins with your students.
- Students can compare their medical knowledge levels with professional levels by adding or removing conditions to these biotwins, examining what should or should not be done for these biotwins at other levels.
- Follow our updates on a biotwin basis due to changes in guidelines. Conduct level reviews for added biobook pages with updates. This way, you will provide your students with the most up-to-date information applied in clinical practice.
